OpenVZ vs KVM VPS: Which Virtualization Technology Should You Choose?
- October 22, 2025
- 0 Comments
Choosing between OpenVZ and KVM VPS is a key decision when setting up a virtual server. These two virtualization technologies power most VPS hosting platforms today, and each offers distinct advantages depending on your goals, resource needs, and control preferences.
In this detailed guide, we’ll break down everything in simple terms — what they are, how they differ, and which one suits your website or business the best.
What is VPS Hosting?
A Virtual Private Server (VPS) gives you the best of both worlds — the affordability of shared hosting and the power of a dedicated server.
Instead of renting an entire server, you get your own virtual environment on a shared machine. This environment has dedicated RAM, CPU, and storage, which ensures consistent performance without being affected by other users.
For example, if you run an e-commerce store or a growing business website, a VPS gives you faster loading speeds, more security, and the ability to install custom software — all at a reasonable cost.
Understanding Virtualization
At the core of VPS hosting lies virtualization technology — the process that splits one physical server into multiple virtual servers. Each of these virtual servers (VPS) acts independently, even though they share the same physical resources.
A special software layer called the hypervisor handles this resource distribution. It ensures that each VPS gets its assigned CPU, RAM, and disk space while maintaining stability across all environments.
Different hosting setups use different virtualization methods — and that’s where OpenVZ and KVM come into play. Both are Linux-based, but they differ significantly in how they virtualize resources.
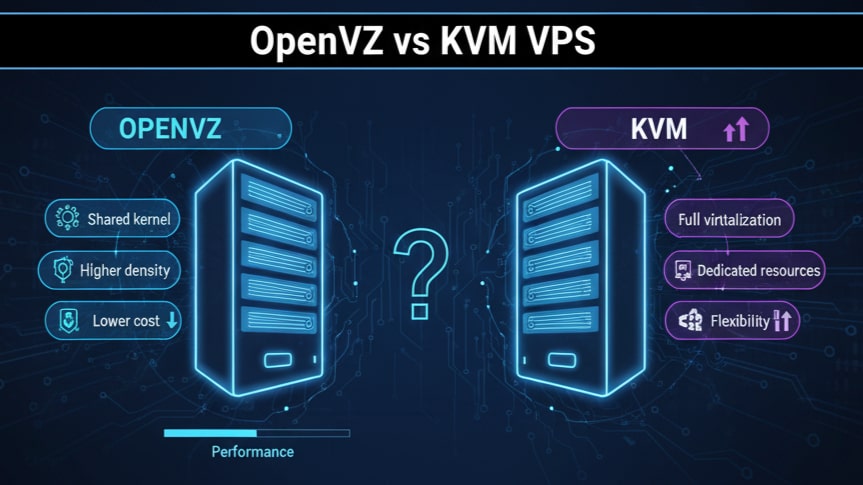
What is OpenVZ?
OpenVZ (Open Virtuozzo) is a container-based virtualization platform for Linux. It divides one physical server into multiple containers, each acting as a standalone system.
However, unlike full virtualization, all these containers share the same Linux kernel as the host. This makes OpenVZ lightweight and resource-efficient but limits flexibility.
Each container can run its own applications, users, and files, but they can’t use a different OS kernel from the host.
Key Features of OpenVZ
- Lightweight Performance: Since all containers share one kernel, resource usage stays minimal.
- High Density: A single server can host many OpenVZ containers efficiently.
- Faster Boot Times: Containers start almost instantly due to shared resources.
- Cost-Effective: Less overhead means cheaper VPS hosting.
- Limited Flexibility: You can only run Linux-based operating systems with the same kernel version.
What is KVM?
KVM (Kernel-based Virtual Machine), on the other hand, is a full virtualization solution. It turns a Linux system into a complete hypervisor, allowing multiple virtual machines to run independently with their own kernels.
This independence allows each VPS to install any OS — Linux, Windows, BSD, or others — and manage it without restrictions.
Think of KVM as having multiple dedicated servers running inside one physical machine — each with full control over its environment.
Key Features of KVM
- True Isolation: Each VPS operates independently with its own kernel and memory.
- OS Flexibility: Supports a wide range of operating systems, not just Linux.
- Complete Control: You can modify kernel settings, install custom modules, or configure low-level system tools.
- Enhanced Security: Since each machine is fully separated, there’s minimal risk of data leakage or system interference.
- Scalability: Resources can be adjusted without affecting other VPS instances.
OpenVZ vs KVM VPS: Side-by-Side Comparison
| Feature | OpenVZ VPS | KVM VPS |
|---|---|---|
| Virtualization Type | Container-based | Full virtualization |
| Kernel | Shared with host | Independent per VPS |
| Operating System Support | Linux only | Linux, Windows, BSD, others |
| Resource Allocation | Shared dynamically | Dedicated and fixed |
| Performance | Faster but limited by shared kernel | More stable, consistent performance |
| Isolation | Partial | Complete |
| Security | Moderate (shared kernel) | Strong (full isolation) |
| Customization | Limited | Full control with root access |
| Use Case | Small projects, lightweight apps | Professional, enterprise, or data-driven workloads |
| Cost | Budget-friendly | Slightly higher, but better value |
Performance Comparison
When we talk about performance, OpenVZ and KVM behave differently.
OpenVZ is efficient because it skips hardware emulation — meaning processes run faster and use less memory. However, since all containers share the same kernel, if one user consumes too many resources, others may experience slowdowns.
KVM, in contrast, assigns dedicated resources to every VPS. Your CPU, RAM, and disk aren’t shared, so your performance stays consistent — even under heavy workloads.
If you’re running a database, streaming app, or a busy website, KVM’s isolation ensures stability and uptime.
Flexibility and Customization
This is where KVM shines the most. It gives you full freedom to install your preferred OS, modify kernel settings, and fine-tune server performance.
OpenVZ, while simpler, is more restrictive. It doesn’t support non-Linux OS or major kernel changes, making it unsuitable for projects needing specific environments or advanced software compatibility.
If you need root-level control or plan to scale your business applications, KVM VPS is the right fit.
Security and Reliability
Security is a top concern for any business hosting online assets.
Because OpenVZ uses a shared kernel, a vulnerability or misconfiguration in one container could theoretically affect others. While modern OpenVZ setups are quite secure, the shared design still introduces minor risk.
KVM eliminates this problem by isolating each VPS completely. Each instance has its own kernel, users, and file system, preventing cross-contamination.
This isolation also improves reliability — even if another VPS crashes or gets attacked, your server stays safe and unaffected.
Pricing and Cost Efficiency
OpenVZ VPS hosting is typically more affordable, as it uses fewer resources per container and allows higher density on one physical server. It’s perfect for personal projects, test environments, or startups just beginning their hosting journey.
KVM VPS is slightly more expensive, but it offers long-term value. You get dedicated performance, freedom, and scalability — all of which save time and cost in the long run.
If you’re serious about uptime, security, and flexibility, the small price difference is worth it.
Real-World Use Cases
Here’s how you can decide which virtualization suits your situation best:
- Choose OpenVZ VPS if you:
- Run small websites, blogs, or forums.
- Have limited technical needs or are new to VPS hosting.
- Need fast and affordable hosting for short-term projects.
- Choose KVM VPS if you:
- Run web apps, databases, or high-traffic sites.
- Need guaranteed resources for performance consistency.
- Require advanced configurations or custom software setups.
- Handle sensitive data and want strict isolation.
How LunarVPS Delivers the Best VPS Experience
At LunarVPS, we believe that performance, reliability, and support are the three pillars of great VPS hosting.
Our KVM VPS solutions are powered by enterprise-grade hardware, SSD/NVMe storage, and high-speed connectivity — ensuring unmatched performance for all workloads.
We offer flexible plans that fit every budget, from developers experimenting with applications to large enterprises scaling global projects.
Plus, with 24/7 technical assistance, advanced DDoS protection, and instant scalability, you’re not just renting a server — you’re getting a full hosting ecosystem designed for growth.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is the main difference between OpenVZ and KVM VPS?
OpenVZ uses container-based virtualization with a shared Linux kernel, making it lightweight and fast. KVM provides full virtualization with independent kernels and dedicated resources, offering more control and stability.
2. Can I run Windows on OpenVZ?
No. OpenVZ only supports Linux distributions because all containers share the host’s Linux kernel. KVM VPS allows Windows, Linux, and other OS installations.
3. Which VPS performs better?
For lightweight applications, OpenVZ can be faster due to minimal virtualization overhead. However, KVM provides consistent, stable performance under heavy workloads, making it better for business-critical applications.
4. Which VPS is more secure?
KVM VPS is more secure because each VPS is fully isolated with its own kernel. OpenVZ is moderately secure but shares the host kernel, which could potentially affect all containers if a vulnerability occurs.
5. Which VPS is better for beginners?
OpenVZ is simpler and more affordable, making it ideal for beginners, personal projects, and small websites.
6. Is KVM VPS worth the extra cost?
Yes. KVM VPS offers dedicated resources, full control, OS flexibility, and stronger security, providing long-term value for businesses and high-performance applications.
Conclusion
Both OpenVZ and KVM VPS have their own strengths. OpenVZ offers simplicity, speed, and affordability — perfect for beginners or small-scale needs.
KVM, however, provides full control, strong security, and dedicated performance — ideal for professionals and businesses that demand stability.
At LunarVPS, we recommend KVM VPS hosting for users who value independence, reliability, and long-term scalability.
👉 Discover the power of KVM VPS hosting at LunarVPS.com — and take your website or business to the next level with cutting-edge virtualization technology.



